19. 删除链表中的倒数第N个节点
题目描述
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
思路
计算链表长度
删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点操作就等价于删除正数第L-n+1个节点,L为链表的长度栈
遍历链表的同时将所有节点依次入栈,根据栈 先进后出 的原则,弹出栈的第n个节点就是需要删除的节点,并且弹出
第n个节点后的栈顶节点为待删除节点的前驱节点。
题目描述:
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
三数之和
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
代码
class Solution:
# 三重循环
def threeSum1(self, nums):
nums.sort()
n = len(nums)
result = []
for first in range(0, n):
if first == 0 or nums[first] != nums[first - 1]:
for second in range(first + 1, n):
if second == first + 1 or nums[second] != nums[second - 1]:
for third in range(second + 1, n):
if third == second + 1 or nums[third] != nums[third - 1]:
if nums[first] + nums[second] + nums[third] == 0:
result.append([nums[first], nums[second], nums[third]])
return result
# 排序+双指针
def threeSum(self, nums):
n = len(nums)
nums.sort()
ans = list()
# 枚举 a
for first in range(n):
# 需要和上一次枚举的数不相同
if first > 0 and nums[first] == nums[first - 1]:
continue
# c 对应的指针初始指向数组的最右端
third = n - 1
target = -nums[first]
# 枚举 b
for second in range(first + 1, n):
# 需要和上一次枚举的数不相同
if second > first + 1 and nums[second] == nums[second - 1]:
continue
# 需要保证 b 的指针在 c 的指针的左侧
while second < third and nums[second] + nums[third] > target:
third -= 1
# 如果指针重合,随着 b 后续的增加
# 就不会有满足 a+b+c=0 并且 b<c 的 c 了,可以退出循环
if second == third:
break
if nums[second] + nums[third] == target:
ans.append([nums[first], nums[second], nums[third]])
return ans
if __name__ == "__main__":
slt = Solution()
nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4]
# res = slt.threeSum(nums)
res = slt.threeSum1(nums) # [[-1, -1, 2], [-1, 0, 1]]
print(res)
| 垃圾收集器 | 串行/并行/并发 | 新生代/老年代 | 算法 | 目标 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serial | 串行 | 新生代 | 复制算法 | 响应速度优先 | 单CPU环境下的Client模式 |
| Serial Old | 串行 | 老年代 | 标记-整理 | 响应速度优先 | 单CPU环境下的Client模式、CMS的后备预案 |
| ParNew | 并行 | 新生代 | 复制算法 | 响应速度优先 | 多CPU环境下在Server模式下与CMS配合 |
| Parallel Scavenge | 并行 | 新生代 | 复制算法 | 吞吐量优先 | 在后台运算而不需要太多交互任务 |
| Parallel Old | 并行 | 老年代 | 标记整理 | 吞吐量优先 | 在后台运算而不需要太多交互任务 |
| CMS | 并发 | 老年代 | 标记-清除 | 响应速度优先 | 集中在互联网网站或者基于浏览器的B/S系统的服务端上的Java应用 |
| G1 | 并发 | Both | 标记-整理+复制算法 | 响应速度优先 | 面向服务端应用,将来替换CMS |
| Shenandoah | 并发 | Both | 标记-整理+复制算法 | 低延迟 | |
| ZGC | 并发 | Both | 标记-整理+复制算法 | 低延迟 |
线程池的实现原理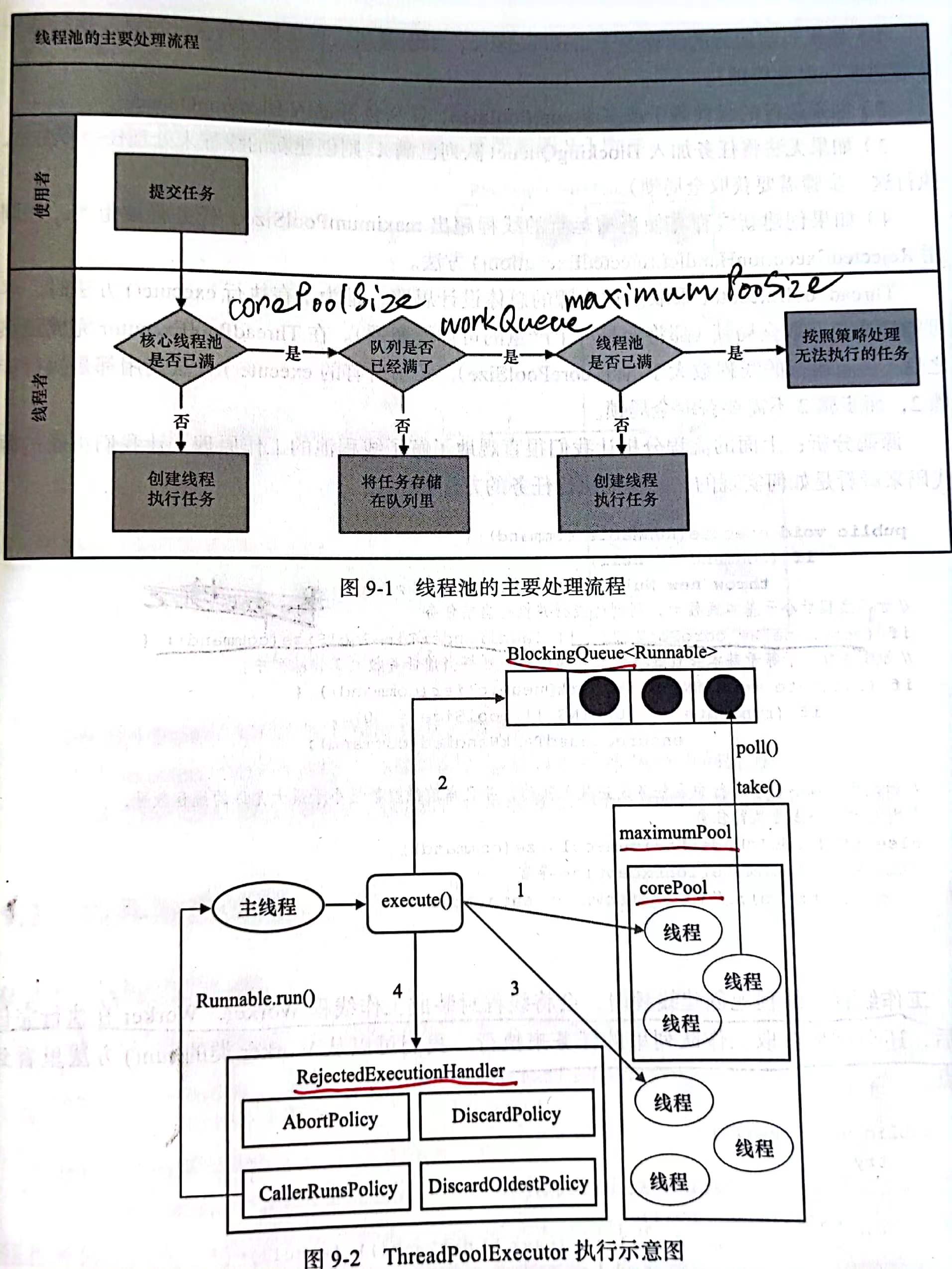
线程池的使用
(1)线程池的创建
new ThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime,unit,workQueue, handler)
Parameters:
corePoolSize: the number of threads to keep in the pool, even if they are idle, unless allowCoreThreadTimeOut is set
maximumPoolSize: the maximum number of threads to allow in the pool
keepAliveTime: when the number of threads is greater than the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads will wait for new tasks before terminating.
unit the time: unit for the keepAliveTime argument
workQueue:the queue to use for holding tasks before they are executed. This queue will hold only the Runnable tasks submitted by the execute method.
threadFactory: set thread factory
handler: the handler to use when execution is blocked because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached
workQueue:
ArrayBlockingQueue:基于数组结构的有界阻塞队列
LinkedBlockingQueue:基于链表结果的阻塞队列
SynchronousQueue:不存储元素的阻塞队列
PriorityBlockingQueue:具有优先级的无限阻塞队列
handler:
AbortPolicy:直接抛出RejectedExecutionException异常
CallerRunsPolicy:使用调用者所在线程来执行任务
DiscardOldestPolicy:丢弃掉在队列中存在时间最久的任务
DiscardPolicy:默认丢弃任务,不进行任何通知
Exchanger用于进行线程间的数据交换。它提供一个同步点,在这个同步点,两个线程可以交换彼此的数据。这两个线程
通过exchange方法交换数据,如果第一个线程先执行exchange方法,它会一直等待第二个线程也执行exchange方法,当
两个线程都到达同步点时,这两个线程就可以交换数据,将本线程生产出来的数据传递给对方。
应用场景
(1)遗传算法
遗传算法里需要选出两个人作为交配对象,这时候会交换两个人的数据,并使用交叉规则得出2个交配结果。
(2)校对工作
例如,我们需要将纸制银行流水通过人工的方式录入成电子银行流水,为了避免错误,采用AB岗两个人进行录入,录入到
Excel后,系统需要加载这两个Excel,并对两个Excel数据进行校对,看看是否录入一致。
示例代码:
package concurrency.exchanger;
import java.util.concurrent.Exchanger;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ExchangerTest {
private static final Exchanger<String> exgr = new Exchanger<String>();
private static ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
public static void main(String[] args) {
threadPool.execute(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
try{
String A = "银行流水A";//A录入银行流水数据
exgr.exchange(A);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
threadPool.execute(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
try{
String B = "银行流水B";//B录入银行流水数据
String A = exgr.exchange(B);
System.out.println("A和B数据是否一致:"+A.equals(B)+",A录入的是:"+A+",B录入的是:"+B);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
Semaphore(信号量)是用来控制同时访问特定资源的数量,它通过协调各个线程,以保证合理的使用公共资源。
应用场景:
Semaphore可以用于做流量控制,特别是公共资源优先的应用场景,比如数据库连接。
示例代码:
package concurrency.semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
public class SemaphoreTest {
private static final int THREAD_COUNT = 30;
private static ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(THREAD_COUNT);
private static Semaphore s = new Semaphore(10);
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 0; i < THREAD_COUNT; i++){//虽然有30个线程在执行,但是只允许10个并发执行
threadPool.execute(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
try{
s.acquire();
System.out.println("save data");
s.release();
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
在java.util.concurrent.atomic包中包含了12个原子类,属于四种类型的原子更新方式,分别是:
(1)原子更新基本类型
AtomicInteger:原子更新整型;
AtomicBoolean:原子更新布尔类型;
AtomicLong:源自更新长整型。
(2)原子更新数组
AtomicIntegerArray:原子更新整型数组里的元素;
AtomicLongArray:原子更新长整型数组里的元素;
AtomicReferenceArray:原子更新引用类型数组里的元素
(3)原子更新引用
AtomicReference:原子更新引用类型;
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater:原子更新引用类型里的字段;
AtomicMarkableReference:原子更新带有标记位的引用类型(可以原子更新一个布尔类型的标记位和引用类型)。
(4)原子更新属性(字段)
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater:原子更新整型的字段的更新器;
AtomicLongFieldUpdater:原子更新长整型的字段的更新器;
AtomicStampedReference:原子更新带有版本号的引用类型,能够解决使用CAS进行原子更新时可能出现的ABA问题。
以下给出每个类型的原子更新的一个示例代码: