编译和链接
通过一个代码示例理解编译与链接的过程
安装gcc
1
sudo apt-get install build-essential
编写示例代码
main.c
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
int add(int a, int b);
int main(){
printf("hello,world!\n");
int result = add(5,5);
return 0;
}math.c
1
2
3int add(int a, int b){
return a + b;
}编译示例代码的两个文件main.c和math.c,得到对应的目标文件(Object File)main.o和math.o
注:目标文件是二进制文件,文件格式是ELF(Executable and Linkable Format),ELF格式是linux下所有可执行文件的通用格式。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27gcc -c main.c
gcc -c math.c
file main.o
main.o: ELF 64-bit LSB relocatable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), #not stripped
readelf -h main.o
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF64
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: REL (Relocatable file)
Machine: Advanced Micro Devices X86-64
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x0
Start of program headers: 0 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 672 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 64 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 0 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 0
Size of section headers: 64 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 14
Section header string table index: 131
2
3readelf -S main.o
.text 代码区域
.data 数据区域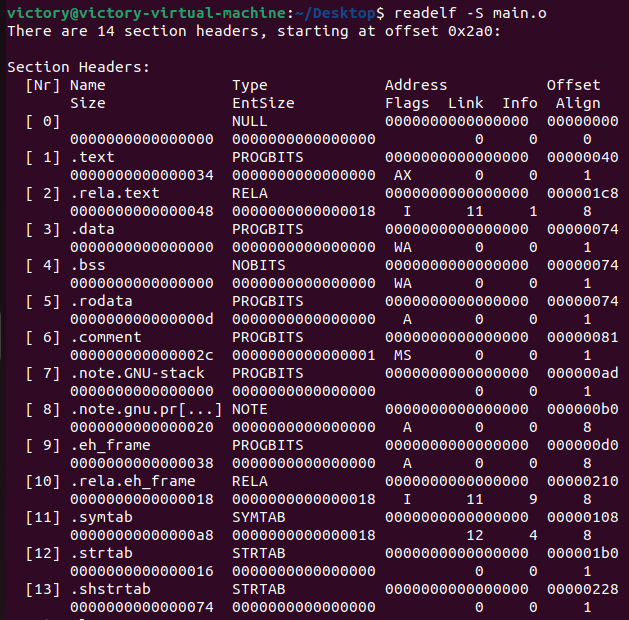
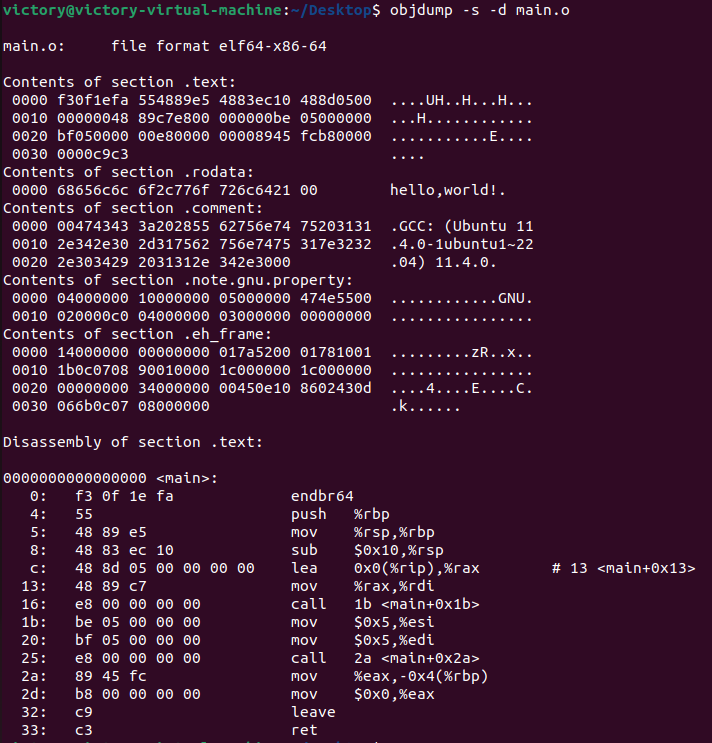
objdump -s -d main.o
-d:将代码段反汇编
-s:将代码段反汇编的同时,将反汇编代码和源代码交替显示,编译时需要给出- g,即需要调试信息。
右侧汇编指令中有两个call指令,既主函数中对printf和add的调用,从机器码可以看出跳转地址为0,需要在后续根据重定位表更新到printf和add的实际地址。
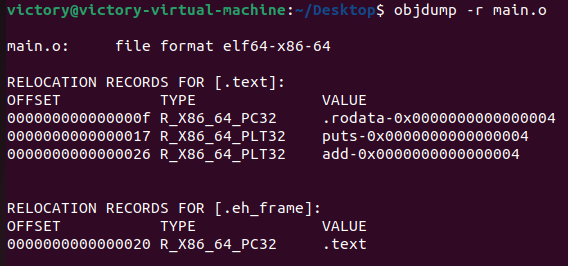
objdump -r main.o
查看两个函数调用的信息(地址偏移量、类型和值)
链接
链接调用的函数机器码并组装为可执行文件main
1
gcc main.o math.o -o main
- 执行可执行文件main
1
2./main
输出hello,world通过makefile来进行编译链接步骤
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13all: main
main: main.o math.o
gcc main.o math.o -o main
main.o: main.c
gcc -c main.c
math.o: math.c
gcc -c math.c
clean:
rm main main.o math.o1
make main