session实现用户登录
下面将使用session实现用户登录,如下图所示效果: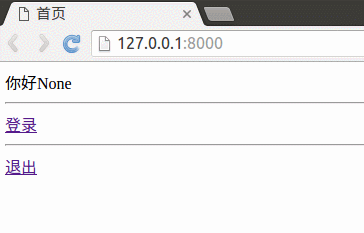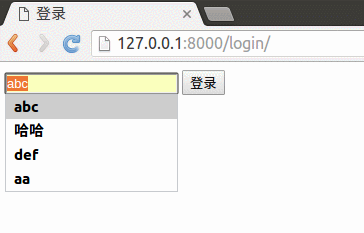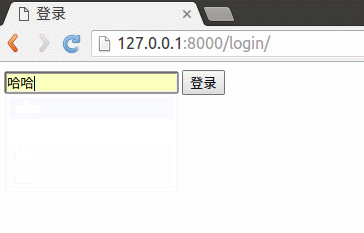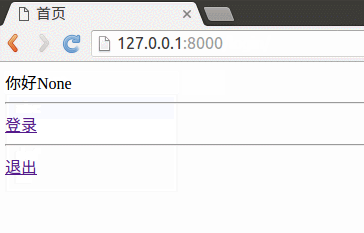
步骤:
1.在views.py文件中创建视图(假定我们创建了一个名为booktest的应用)
def index(request):
uname = request.session.get('myname', default='未登录')
context = {'uname': uname}
return render(request, 'booktest/index.html', context)
def login(request):
return render(request, 'booktest/login.html')
def login_handle(request):
uname = request.POST['uname']
request.session['myname'] = uname
return redirect('/booktest/index/')
def logout(request):
# del request.session['myname'] # 删除会话
# request.session.clear() # 清除所有会话
request.session.flush() # 删除当前的会话数据并删除会话的Cookie
return redirect('/booktest/index/')
2.配置url
主url:
from django.conf.urls import include, url
from django.contrib import admin
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^booktest/', include("booktest.urls", namespace='booktest')),
]
应用url:
from django.conf.urls import include, url
import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^index/$', views.index),
url(r'^login/$', views.login),
url(r'^login_handle/$', views.login_handle),
url(r'^logout/$', views.logout3),
]
3.创建模板
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
你好:{{ uname }}
<br>
<a href="/booktest/session2/">登录</a>
<br>
<a href="/booktest/session3/">退出</a>
</body>
</html>
login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" action="/booktest/session2_handle/">
<input type="text" name="uname">
<input type="submit" name="登录">
</form>
</body>
</html>
4.配置模板路径DIRS
注:templates为和应用同级的文件夹,本应用的模板存在templates/booktest/下
TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')],
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'context_processors': [
'django.template.context_processors.debug',
'django.template.context_processors.request',
'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
],
},
},
]